Table of Contents
What Is the Cell?
There are many definitions for the cell:
The cell is the functional unit of life. The cell is the basic building blocks of all living things, The cell is the structural and fundamental unit of all the living species and many.
Based on the number of cells, organs are further classified into unicellular (single cells) and multicellular (many cells).
Humans are composed of billions to trillions of cells. Every single living cell present within the human body has its own specialized functions. There are no living species existing without the cell.
The group of cells makes up tissue, which makes up organs and a complete organ system.
Based on the number of cells, organs are further classified into unicellular (single cells) and multicellular (many cells).
What are Cell Organelles?
Cell organelles are the structural and functional unit of the cell. All the specialized functions are carried out by a group of specialized organelles, which are present within the cell and enclosed in a membrane. In the cell, these organelles play a vital role by keeping the cell alive and active.
Cell organelles and their Functions
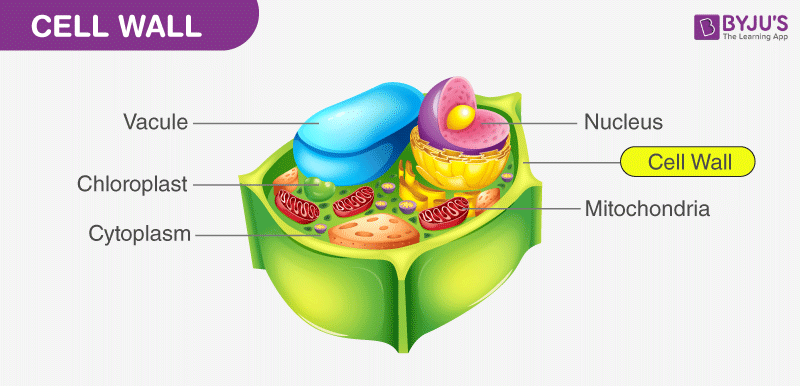
Both plant and animal cells have some different cell organelles. Unlike plant cells, animal cells lack cell walls and plastids.
Let’s learn more about the different cell organelles along with their functions.
Nucleus
It is the largest, double-membrane cell organelle, which is found both in plants, animals and in all eukaryotic cells. It is the storehouse of the cell’s DNA and the control center for all the cellular metabolism. Based on the presence of a true nucleus, there are two main types of cells – the Prokaryotic and the Eukaryotic cell.
Cell membrane
It is the outermost cellular organelle, which is present both in plants and animals. The cell membrane is mainly involved in providing protection for the cell and its cellular components from the external environment.
Mitochondria
It is a double-membrane and an oval-shaped cell organelle, which is mainly responsible for cellular respiration. It is found both in plants, animals and in all eukaryotic cells. It is called “Energy Currency Of the Cell” as it is a storehouse for energy, and stores in the form of ATP – Adenosine Triphosphate molecules.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
It is a network of membranous tubules, which forms a skeletal framework of the cell. It is present within the cytoplasm and mainly involved in excretion of toxins from the cells, along with the production of proteins and lipids.
Golgi Apparatus
It is also termed as Golgi Complex or Golgi bodies. It is a membrane-bound organelle, found in all eukaryotic cells. The Golgi body functions by transporting essential nutrients, proteins and lipids to targeted destinations. Hence, it is also termed as “postman of the cell”.
Cytoplasm
It is a jelly-like substance, found both in plants, animals and in all eukaryotic cells. It mainly consists of water, dissolved nutrients and other waste products of the cell.
This cell organelle is mainly responsible for cellular metabolic activities.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S to learn more in detail about the cells, cell organelles, their structure and function. Also, enjoy by watching various YouTube videos on cells and cell organelles by subscribing to the YouTube Channel.







